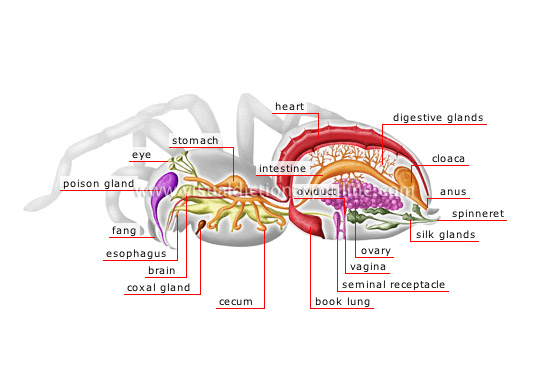
anatomy of a female spider
fang 
Curved part below the eyes and attached to the venom gland; it allows the spider to catch its prey to inject it with venom.
poison gland 
Organ producing an acidic secretion made of venom; it is attached to the fang.
cloaca 
Orifice common to the intestine and the genital and urinary tracts; it is located at the terminal end of the digestive tract.
eye 
Organ of vision joined to the brain by a nerve; the spider usually has four pairs of simple eyes.
stomach 
Dilated section of the digestive tract preceding the intestine; it receives food to be digested.
heart 
Muscular organ helping blood to circulate.
digestive glands 
Organs producing a secretion that contributes to digestion.
anus 
Terminal orifice of the digestive tract enabling ejection of fecal matter.
spinneret 
Appendage located near the anus, where the silk glands end; the spider generally has three pairs.
silk glands 
Silk-secreting organs located in the abdomen and ending in the spinneret.
oviduct 
Canal through which the eggs are expelled from the ovaries.
vagina 
Female organ of copulation located on the ventral face of the abdomen.
ovary 
Female genital gland producing the eggs.
seminal receptacle 
Pouch where sperm is stored for fertilizing the eggs.
book lung 
Respiratory organ that helps to oxygenate the blood; the respiratory system has one or two pairs, depending on the type of spider.
intestine 
Section of the digestive tract between the stomach and the anus where nutrients are absorbed and waste is turned into fecal matter.
cecum 
Lateral canal located in the anterior portion of the intestine where especially a part of digestion and fermentation take place.
brain 
Main organ of the nervous system; it is located in the cephalothorax.
coxal gland 
Organ appended to the hip and producing a secretion that contributes to excretion.
esophagus 
Canal of the anterior portion of the digestive tract; it carries food to the stomach.