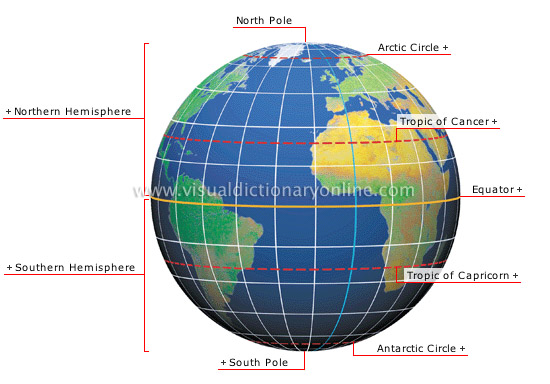
Earth coordinate system
The intersection of two imaginary lines, longitude and latitude, makes it possible to locate a precise point on the Earth’s surface.
Arctic Circle 
Parallel of latitude 66°34' N; it marks the polar zone, where days and nights last 24 hours during solstices.
Tropic of Cancer 
Parallel located at 23°26' N latitude (a distance of about 1,600 mi from the Equator).
Equator 
Imaginary line encircling the Earth at its greatest circumference and perpendicular to the polar axis; its latitude, 0, serves as a reference point for calculating other latitudes.
Tropic of Capricorn 
Parallel located at 23°26' N latitude (a distance of about 1,600 mi from the Equator).
South Pole 
Point on the Earth’s surface at the southern extremity of the axis of rotation, where the meridians converge.
Southern Hemisphere 
Southern half of the globe in relation to the Equator.
Northern Hemisphere 
Northern half of the globe in relation to the Equator.
North Pole 
Point on the Earth’s surface at the northern extremity of the axis of rotation, where the meridians converge.
Antarctic Circle 
Parallel of latitude at 66°34' S; it marks the polar zone, where days and nights last 24 hours during solstices.