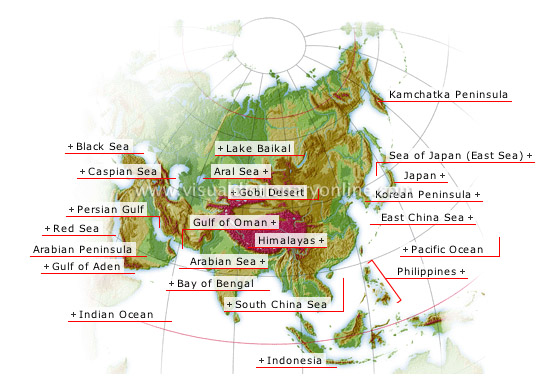
Asia
The largest and most populous continent, Asia represents 32% of the world’s land; it is dominated by imposing mountain ranges.
Caspian Sea 
The world’s largest lake (140,000 mi2), located between Europe and Asia; it has no link to an ocean and is diminishing in size.
Black Sea 
Inland sea (162,000 mi2) between Eastern Europe and Asia; it opens into the Mediterranean through two straits, the Dardanelles and the Bosporus.
Red Sea 
Gulf (165,000 mi2) located between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula; it connects to the Mediterranean through the Suez Canal.
Gulf of Aden 
Northwestern arm of the Indian Ocean between southern Saudi Arabia and northeastern Africa; it connects to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab El Mandeb.
Arabian Peninsula 
Vast semiarid peninsula; it holds 50% of the world’s oil supply.
Persian Gulf 
Gulf (500 mi long) bordered by Saudi Arabia, Iran and Iraq; it is also called the Arabian Gulf and is an important maritime trade route.
Indian Ocean 
Relatively small ocean (29 million mi2) located between Africa, Asia and Australia; it has high water temperatures and is dotted with numerous islands.
Himalayas 
The world’s highest mountain range; it contains some ten peaks above 26,000 feet, including Everest (29,035 feet).
Gulf of Oman 
The narrowest part of the Arabian Sea; it connects to the Persian Gulf through the Strait of Hormuz.
Arabian Sea 
Area of the Indian Ocean between India and the Arabian Peninsula; the Gulf of Oman is an arm of the Arabian Sea.
Bay of Bengal 
Area of the Indian Ocean between India and the Indochinese Peninsula; the Ganges River empties into this bay through the world’s largest delta.
Indonesia 
Archipelago with almost 14,000 islands extending 3,100 mi from west to east; it is the world’s most active volcanic zone.
South China Sea 
Southern part of the China Sea bordering the entire southeast coast of Asia as well as Borneo, the Philippines and Taiwan.
Philippines 
Archipelago with more than 7,000 islands and islets; two principal islands (Luzon and Mindanao) make up 70% of its territory.
East China Sea 
Area of the China Sea between Korea, the Ryukyu Islands (south of Japan) and Taiwan.
Korean Peninsula 
Peninsula that delimits the Sea of Japan; its climate is marked by monsoons in summer and typhoons in the fall.
Japan 
Archipelago made up of 1,000 islands, including four main islands that represent 95% of its territory; it is characterized by intense volcanic activity and frequent earthquakes.
Pacific Ocean 
The world’s largest ocean (69 million mi2), the Pacific covers 30% of the Earth’s surface, more than all of the continents put together.
Sea of Japan (East Sea) 
Area of the Pacific Ocean that separates Japan from the Asian mainland; it is divided into a warm region and a cold region.
Kamchatka Peninsula 
Peninsula (12,000 mi2) on the Bering Sea; it is characterized by intense volcanic activity.
Lake Baikal 
The world’s oldest (25 million years) and deepest (5,315 feet) lake; Lake Baikal is 370 mi long and 40 to 50 mi wide and is frozen six months of the year.
Gobi Desert 
One of the largest deserts in the world (400,000 mi2), shared by China and Mongolia; the Gobi is a plateau situated at an elevation of about 3,300 feet.
Aral Sea 
Sea once connected to the Caspian Sea; it is now an immense salt lake.