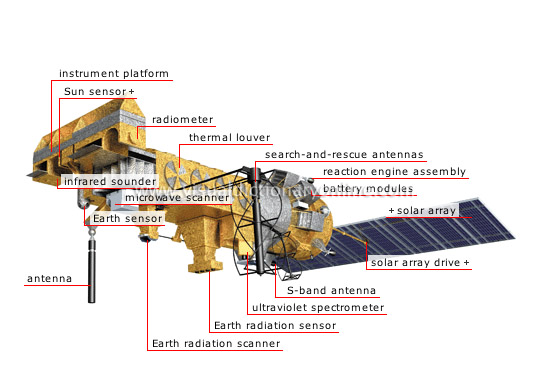
polar-orbiting satellite
Satellite that travels in a polar orbit around the globe 14 times per day; this allows it to cover the entire surface of the globe, due to the Earth’s rotation.
solar array drive 
solar array 
Power supply device that converts solar energy into immediately usable electrical energy.
radiometer 
Instrument designed to measure electromagnetic radiation energy at a given frequency.
thermal louver 
Adjustable mechanical component designed to modify thermal flux.
reaction engine assembly 
Micromotor that makes it possible to direct a satellite to the desired position.
ultraviolet spectrometer 
Instrument that monitors ozone levels in the Earth’s atmosphere.
S-band antenna 
Antenna that enables a satellite to transmit the data it collects to the terrestrial station.
Earth radiation sensor 
Radiometer that measures solar radiation and reflection in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Earth radiation scanner 
Radiometer that analyzes a region of the globe by means of repeated scans.
microwave scanner 
Instrument that produces an image of an observed area even in cloudy conditions since microwave frequencies pass through clouds.
antenna 
Device that emits and receives radio waves.
Earth sensor 
Instrument that locates the Earth’s horizon so that the antenna can be positioned correctly.
infrared sounder 
Instrument that measures thermal energy in clouds and on the Earth’s surface with a view to capturing nighttime images of weather systems and cloud cover.
Sun sensor 
Instrument that positions the solar panels in the direction of the Sun to capture its energy.
search-and-rescue antennas 
Device that picks up distress signals emitted by ships or aircraft and makes it possible to determine their location.
battery modules