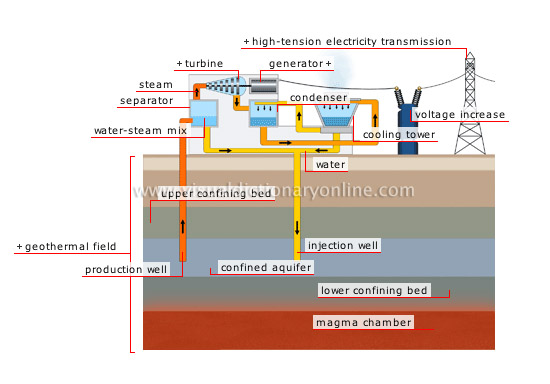
production of electricity from geothermal energy
Hot water contained in the ground near a volcano, geyser or thermal source is piped to the surface by drilling to extract steam and produce electricity.
generator 
Turbine-powered rotating machine that converts mechanical energy into electric energy to direct it toward a transmission network.
production well 
Borehole dug into the ground to allow the hot water contained in the aquifer to be pumped to produce electricity.
geothermal field 
Area of Earth’s crust where a pocket of hot confined water is close enough to the surface to be exploited.
confined aquifer 
Layer of porous sedimentary rock between two impermeable layers where water accumulates at a temperature between 300°F and 750°F.
lower confining bed 
Layer of impermeable rock that transmits heat from the magma chamber to the aquifer.
magma chamber 
Pocket of magma (molten rock emerging from Earth’s crust) that constitutes a heat source; it transmits its thermal energy to water.
upper confining bed 
Layer of impermeable rock that covers the confined aquifer.
separator 
Device that separates water from steam, which it recovers to operate the turbine; the water is reinjected into the aquifer.
turbine 
Steam-powered machine whose wheel transmits mechanical energy to the generator and causes it to rotate.
injection well 
Borehole that is drilled into the ground to return water to the aquifer, where it is reheated after its heat has been extracted.
steam 
Gaseous state of water; steam pressure operates the turbine.
water 
Liquid made up of hydrogen and oxygen that becomes steam at 212°F; the water transfers Earth’s internal heat.
water-steam mix 
Hot water extracted from the aquifer; as it rises to the surface, it is partially turned into steam.
high-tension electricity transmission 
Using high-voltage lines to transmit electricity over long distances reduces the strength of the current and, as a result, energy losses.
voltage increase 
At the outlet end of the power plant, the transformer increases the voltage; this reduces energy losses during transmission over long distances.
cooling tower 
Device that cools the condenser’s hot water on contact with the air; some of the water evaporates and the rest is reinjected into the condenser and the aquifer.
condenser 
Circuit that cools the steam from the turbine and condenses it into water.