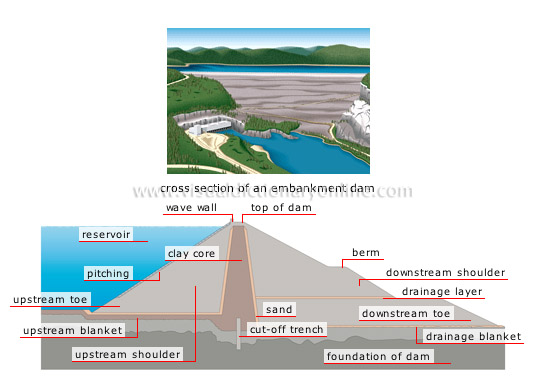
embankment dam
Formed of mounds of earth or rocks, it is used mainly when the subsoil does not allow for construction of a concrete dam.
cross section of an embankment dam 
drainage layer 
Layer of permeable materials that is inserted into large-scale dams to collect infiltrated water.
sand 
Granular material that is inserted between the core and the shoulder; it filters particles carried by the water flow to prevent erosion.
cut-off trench 
Area of the foundation of the dam that is connected to the core; it contains impermeable materials to limit leakage and infiltration under the dam.
upstream blanket 
Impermeable layer that consists of compact clay; it rests on the bottom of the dam to prevent infiltration.
foundation of dam 
Natural terrain (such as rock, sand or clay) on which the dam is built.
downstream shoulder 
Soil embankment that, together with the upstream shoulder, provides stability to the structure.
drainage blanket 
Layer of permeable materials on the foundation of the dam; it collects infiltrated water and prevents erosion of the base of the dam.
upstream shoulder 
Soil embankment located on the reservoir side; its mass provides stability to the dam.
upstream toe 
Area where the upstream shoulder and the foundation of the dam meet.
downstream toe 
Area where the downstream shoulder and the foundation of the dam meet.
berm 
Horizontal ledge that stabilizes the upstream or downstream shoulder.
reservoir 
Basin formed by the construction of a dam; it holds back a very large volume of water so that the flow rate can be controlled.
wave wall 
Small wall located at the top of the upstream shoulder that protects the dam against waves.
pitching 
Layer of rock or concrete blocks that covers the upstream shoulder to prevent erosion.
clay core 
Central portion of the dam that is usually made of compact clay to make it watertight.
top of dam 
Upper part of the dam; it rises above the water level of the reservoir by several yards.