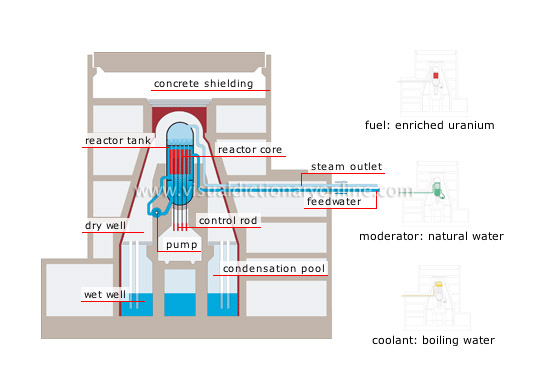
boiling-water reactor
In this second most common reactor, boiling occurs directly in the reactor core; it is used mainly in the United States, Sweden and Japan.
steam outlet 
Steam produced in the reactor tank is carried to the turbine to produce electricity.
concrete shielding 
Concrete structure that holds back radioactive products in the event of an accident.
condensation pool 
Water-filled basin that is used to lower the pressure in the reactor tank in the event of an accident.
dry well 
Compartment around the reactor tank; it holds back radioactive products in the event of an accident.
control rod 
Tube that contains a neutron-absorbing material (boron, cadmium) that is introduced into the reactor core to control its power.
pump 
Device that continuously circulates water inside the reactor.
reactor core 
Center section of the nuclear reactor where fission reactions take place.
reactor tank 
Safety containment wall that separates the reactor from the rest of the building.
feedwater 
Piping that carries water from the condenser into the reactor tank, where it is converted into steam.
wet well 
Compartment containing water that reduces the pressure in the dry well in the event of an accident.
coolant: boiling water 
Boiling water: natural water that boils and vaporizes on contact with the heat released by the fuel.
fuel: enriched uranium 
Enriched uranium: uranium produced by treating natural uranium to increase the quantity of fissionable isotopes (uranium-253) contained in it.
moderator: natural water 
Natural water: water found in its natural state.