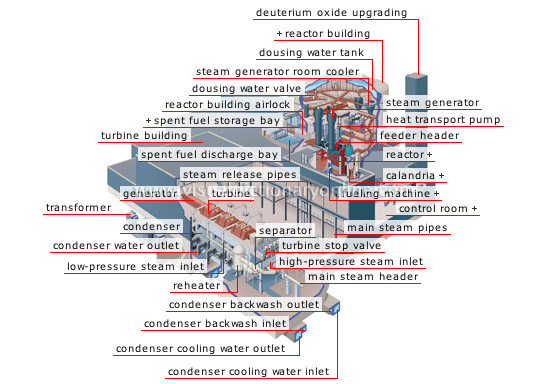
nuclear generating station
Plant that produces electricity from thermal energy generated by the fission of fuel atoms in a reactor.
high-pressure steam inlet 
Steam from the steam generators is carried to the first section of the turbine; here, it cools down and loses some of its energy.
separator 
Device that removes any water from the steam to prevent damage to the turbine’s runner.
turbine stop valve 
Device that blocks steam from entering the turbine.
reheater 
Device used to increase the temperature of the steam from the first section of the turbine to reinject it into the second section.
condenser water outlet 
Water in the condenser returns to its original source.
low-pressure steam inlet 
Heated steam is reinjected into the turbine, where it releases its remaining energy.
condenser 
Water collected from the water table flows in a circuit to cool the steam from the turbine and condense it into water.
turbine 
Machine in two sections whose steam-activated runner transmits mechanical energy to the rotor shaft of the generator.
generator 
Turbine-powered rotating machine that converts mechanical energy into electric energy to direct it toward a transmission network.
turbine building 
Enclosure housing the devices (turbines and generator) used to produce electricity.
spent fuel discharge bay 
Water-filled basin that receives spent fuel as it exits the accept machine; the water acts as a protective barrier against the radiation emitted by the fuel.
reactor building airlock 
Secure area where equipment and personnel can pass safely through the reactor building.
dousing water valve 
Device that releases water from the dousing water tank in the reactor building to condense the radioactive steam.
steam generator 
Apparatus that turns water into steam, which in turn activates the turbine.
dousing water tank 
Vat that contains water to cool the radioactive steam in the reactor in the event of an accident; this prevents a rise in pressure.
reactor building 
Concrete structure surrounding the reactor vessel; it is a protective barrier against radioactivity.
steam generator room cooler 
Cooling system that controls the temperature of the room housing the generators.
deuterium oxide upgrading 
In power stations where heavy water is used as a moderator, a filter holds back steam (deuterium oxide) at the mouth of the stack.
heat transport pump 
Apparatus that circulates the coolant fluid between the reactor and the steam generator.
reactor 
Tightly sealed area where fission of the fuel is carried out in a controlled manner to release heat.
calandria 
Safety containment wall that separates the reactor from the rest of the building.
fueling machine 
Remote-controlled cylinder used to load and unload the reactor.
control room 
Area that houses the personnel and equipment used to operate and monitor the power station.
steam release pipes 
All the pipes used to carry steam to the separator outlet.
main steam pipes 
All the pipes used to carry steam to the steam generator outlet.
main steam header 
Device that collects and disperses steam from the steam generators.
condenser backwash outlet 
Channel through which condensed water from the steam in the turbine returns to the water table.
condenser cooling water inlet 
Channel through which water from a watercourse is pumped into the condenser.
condenser backwash inlet 
Inlet channel for the water needed for the condensation circuit of the steam in the turbine.
condenser cooling water outlet 
Channel through which the water from the condenser returns to the watercourse from which it came.
spent fuel storage bay 
Water-filled basin where the spent fuel is stored for several years before it can be disposed of safely.