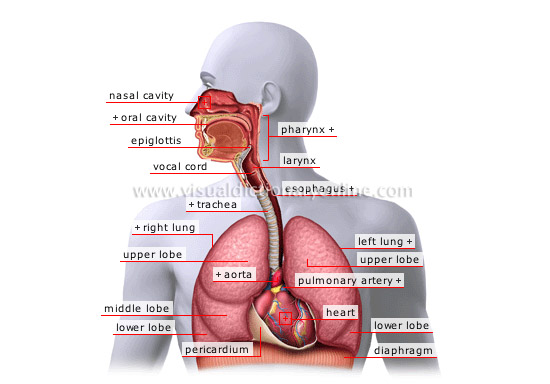
respiratory system
It causes gaseous exchanges to take place in the lungs by ensuring that oxygen is carried to the blood through inspiration, and carbon dioxide is eliminated from the blood through expiration.
El Diccionario Visual, a new valuable resource to learn Spanish. Includes 17 all-around themes to explore, including the human body, sciences and food.
epiglottis 
Movable cartilaginous plate ensuring that the larynx closes during ingestion of food so that food cannot enter the respiratory tract.
pharynx 
Muscular membranous channel connecting the nasal cavity to the larynx and the oral cavity to the esophagus; it enables breathing, ingestion of food and speech.
esophagus 
Muscular membranous channel of the anterior section of the digestive tract; it allows food to reach the stomach.
trachea 
Muscular cartilaginous tract that is a continuation of the larynx; it divides into two main bronchi, each of which ends in a lung, and allows air to pass.
left lung 
Respiratory organ divided into two lobes where blood from the pulmonary artery is cleansed of carbon dioxide and enriched with oxygen.
pulmonary artery 
Artery carrying blood that is poor in oxygen and rich in carbon dioxide to the lungs; it is the only artery that transports oxygen-poor blood.
upper lobe 
Section of the left lung separated from the lower lobe by the oblique fissure.
aorta 
Main artery of the body that originates in the left ventricle of the heart and is made up of four segments; it distributes oxygenated blood throughout the body.
lower lobe 
Section of the left lung separated from the upper lobe by the oblique fissure.
diaphragm 
Main muscle of inspiration separating the thorax from the abdomen; its contraction increases the size of the thoracic cage and lungs, into which inhaled air is carried.
heart 
Muscular organ divided into four chambers; its regular rhythmic contractions cause blood to circulate throughout the organism.
pericardium 
Exterior casing of the heart formed of an inner layer adhering to the myocardium and a thick fibrous outer layer.
lower lobe 
Section of the right lung separated from the middle and upper lobes by an oblique fissure.
middle lobe 
Section of the right lung separated from the upper lobe by a horizontal fissure and from the lower lobe by an oblique fissure.
upper lobe 
Section of the right lung separated from the middle lobe by a horizontal fissure and from the lower lobe by an oblique fissure.
right lung 
Respiratory organ divided into three lobes in which blood from the pulmonary artery is cleansed of carbon dioxide and enriched with oxygen.
vocal cord 
Muscular fold aiding speech; the vocal cords close and vibrate when air is expelled from the lungs, thereby producing sound.
larynx 
Muscular cartilaginous duct at the upper terminal part of the trachea; it contains the vocal cords and plays a role in speech and respiration.
oral cavity 
Secondary entry point of the respiratory system (physical effort, partial obstruction of the nose); it also helps the ingestion of food.
nasal cavity 
Place where air inhaled through the nostrils is filtered and humidified; it also plays an olfactory role.