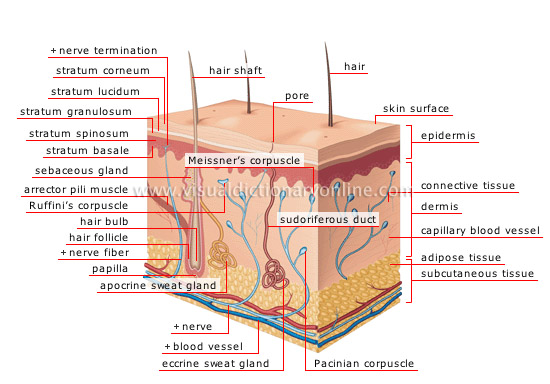
skin
Outer covering of the body consisting of three layers; it has a role in protection, tactile sensation and thermoregulation.
subcutaneous tissue 
Tissue rich in veins and nerves at the base of the dermis enabling especially the absorption of shocks.
capillary blood vessel 
Very fine blood vessel connected to the arterial and venal networks; through it the blood and cells of the organism are exchanged.
dermis 
Layer of skin enclosing tactile receptors ensuring nutrition and support of the epidermis.
connective tissue 
Tissue rich in veins and nerves made up especially of collagen and elastin fibers that give the skin its elasticity and resistance.
epidermis 
Surface layer of the skin covering and protecting the dermis; it contains proteins that make the skin impermeable and block ultraviolet rays.
skin surface 
Surface portion of the skin in contact with the air from which dead cells are regularly shed and replaced by new cells of the stratum basale.
adipose tissue 
Tissue enclosing numerous fat cells, thermally insulating the organism and providing an energy reserve.
Pacinian corpuscle 
Tactile receptor implanted in the deep dermis; it reacts to continuous vibrations and strong pressures.
eccrine sweat gland 
Sweat-secreting organ whose excretory duct opens onto the surface of the skin; the sweat glands help especially in the elimination of waste.
sudoriferous duct 
Duct carrying sweat produced by the sweat gland to the surface of the skin.
apocrine sweat gland 
Sweat-secreting organ whose excretory duct opens into the hair follicle.
blood vessel 
Membranous canal through which blood circulates in the organism, bringing in oxygen and nutrients and carrying away waste.
nerve 
Bundle of nerve fibers carrying sensory information collected by the tactile receptors of the brain.
papilla 
Cone-shaped formation borne by the dermis ensuring vascularization of the hair.
nerve fiber 
Structure formed of neuron extensions along which the skin’s sensory information travels.
hair bulb 
Enlarged terminal part of the follicle from which hair develops and whose base receives the papilla.
hair follicle 
Small cavity of the dermis and hypodermis in which the hair root is implanted and which receives secretions from the sebaceous and sweat glands.
sebaceous gland 
Organ connected to a hair follicle secreting a fatty substance (sebum) that lubricates the hair and skin, making them impermeable to air and water.
arrector pili muscle 
Muscle attached to a hair follicle and whose contraction raises the hair on end as a result of cold or fear.
nerve termination 
Tactile receptor present in large numbers on the surface of the dermis.
stratum basale 
Layer of the epidermis whose cells divide and migrate toward the surface to form the upper layers, thus ensuring renewal of the epidermis.
stratum spinosum 
Layer of the epidermis consisting of cells from the stratum basale, which continue to divide to form the stratum granulosum.
stratum granulosum 
Layer of the epidermis whose cells help to form keratin, which renders the skin impermeable.
stratum lucidum 
Layer of the epidermis usually present only in the thick skin of the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
stratum corneum 
Layer of the epidermis consisting of dead cells rich in keratin (the protein that protects the skin); it is shed as a new layer is formed.
hair shaft 
External portion of the hair at the narrow terminal part.
Ruffini’s corpuscle 
Heat-sensitive tactile receptor present in large numbers in the dermis of the hairy regions; it reacts especially to firm continuous pressure.
hair 
Threadlike epidermal outgrowth present on almost the entire body having a sebaceous gland and an arrector pili muscle; it plays a protective role.
pore 
Orifice in which the sweat duct opens, allowing excretion of sweat onto the surface of the skin.
Meissner’s corpuscle 
Tactile receptor located especially at the level of the superficial dermis of the hands, feet, lips and genital organs; it is sensitive to light touching.