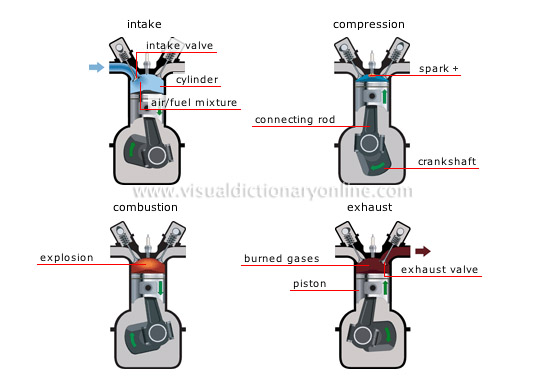
four-stroke-cycle engine
Combustion engine whose cycle (intake, compression, combustion, exhaust) requires two up-and-down movements of the piston.
exhaust 
Phase during which the exhaust valve opens and the piston moves back up to expel the burned gases.
burned gases 
Mixture of gases (carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide and unburned hydrocarbons) filling the combustion chamber after the explosion.
exhaust valve 
Part that opens to allow the burned gases to escape.
piston 
Metal moving part in the cylinder and attached to the connecting rod; it compresses the air/fuel mixture, then receives the thrust from the burned gases.
combustion 
Phase during which the expansion of the combustion gases pushes the piston downward, driving the rotation of the crankshaft.
explosion 
Ignition of the air/fuel mixture produces a major energy release that pushes the piston downward.
intake 
Phase during which the exhaust valve opens and the piston comes down and draws the air/fuel mixture into the combustion chamber.
cylinder 
Chamber closed by two valves; in it, the piston moves and the air/fuel mixture is burned.
air/fuel mixture 
Mixture prepared in the carburetor, containing an amount of fuel proportional to the amount of air entering.
intake valve 
Part that opens to let the air/fuel mixture into the cylinder.
compression 
Phase during which the piston goes up to compress the air/fuel mixture. At the height of the compression, the spark plug produces a spark.
spark 
Spark produced when an electric current arcs between the two electrodes of a spark plug and ignites the air/fuel mixture.
crankshaft 
Shaft consisting of a series of cranks, which convert the alternate rectilinear motion of the piston/connecting rod assembly into a continuous circular motion.
connecting rod 
Articulated shank powered by the gas explosion; it transmits the thrust from the piston to the crankshaft.