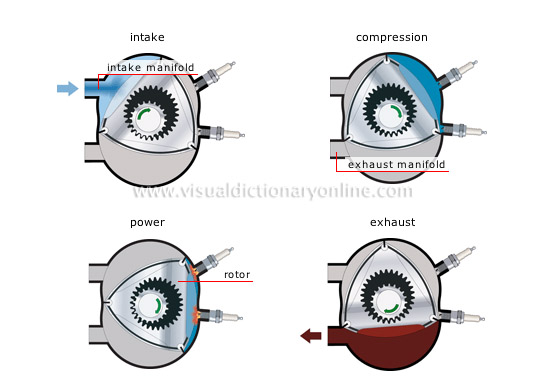
rotary engine cycle
Rotary engine: combustion engine in which the combustion chamber is divided by a rotor into three turning parts of unequal volume.
intake 
The air/fuel mixture enters the cylinder through the intake manifold; the rotor’s motion forces it into the next chamber.
intake manifold 
Passages through which the air/fuel mixture enters the cylinder.
power 
When the compression level is reached, the spark plugs produce sparks that ignite the air/fuel mixture.
rotor 
Triangular piston turning eccentrically around an axle and transmitting a rotational motion directly to the crankshaft.
exhaust 
In the passage before the exhaust manifold, the burned gases are expelled by the rotor.
compression 
The rotor’s rotation reduces the volume in the chamber and compresses the mixture.
exhaust manifold 
Pipe through which the burned gases are expelled from the cylinder.