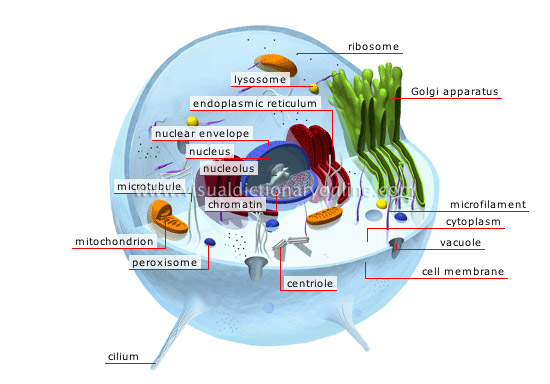
animal cell
Smallest living structure and constituent unit of all animals, including human beings; its size and shape vary according to function.
microtubule 
Cylindrical structure supporting the cell and allowing organelles and substances inside the cell to move about.
cilium 
Filament-like extension of the cytoplasmic membrane allowing the cell and certain substances on its surface to move about.
microfilament 
Rod-shaped structure supporting the cell and giving it its shape.
peroxisome 
Organelle containing enzymes that neutralize the cell’s toxic substances.
cell membrane 
The cell’s flexible outer casing; it separates the cell from the surrounding environment and works as a filter to control the entry and exit of certain substances.
chromatin 
Mass of very fine filaments of DNA, the genetic material of the cell; it is compressed into chromosomes during cell division.
nucleus 
Organelle containing a cell’s genes and controlling its activities.
ribosome 
Organelle, free or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, producing proteins essential to the constitution and functioning of living beings.
endoplasmic reticulum 
Organelle formed of walls to which the ribosomes are attached.
mitochondrion 
Ovoid organelle that produces the energy necessary for cell activity.
cytoplasm 
Clear gelatinous substance surrounding the various cellular structures.
vacuole 
Spherical cavity containing water, waste and various substances required by the cell.
lysosome 
Small spheroid organ containing enzymes that break down food, spent cell components and other harmful substances that have been absorbed.
nuclear envelope 
Envelope formed of two layers surrounding the nucleus and pierced with small holes, which allow exchanges between the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
nucleolus 
Small spherical body located inside the nucleus, within which the ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures, are produced.
centriole 
Structure consisting of small rods that play a major role in cell division. Each cell usually contains two.
Golgi apparatus 
Organelle composed of a series of pockets that receive proteins produced by the ribosomes and either transport them outside the cell or to other organelles.