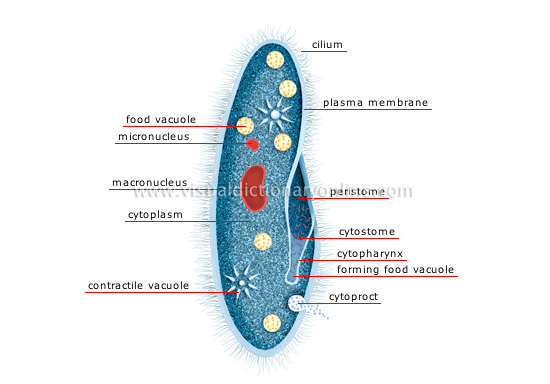
paramecium
Ovoid-shaped one-cell organism generally found in freshwater and covered with cilia, which allow it to move about and to feed, mainly on bacteria.
cilium 
Filament-like extension of the cytoplasmic membrane allowing the cell and certain substances on its surface to move about.
plasma membrane 
The cell’s flexible outer casing; it separates the cell from the surrounding environment and works as a filter to control the entry and exit of certain substances.
peristome 
Depression lined with cilia, which undulate to direct food particles toward the cytostome.
cytostome 
Opening corresponding to the mouth and allowing ingestion of food and rejection of undesirable elements.
cytopharynx 
Fold of the plasma membrane; food particles originating in the cytostome are directed toward it.
cytoproct 
Orifice corresponding to the anus; the food vacuole opens into it, allowing waste to be eliminated.
contractile vacuole 
Spheroid cavity acting as a pump to evacuate excess water and waste from the cell.
cytoplasm 
Clear gelatinous substance surrounding the various cellular structures.
macronucleus 
Large nucleus controlling cellular activities.
micronucleus 
Small nucleus ensuring cell reproduction.
food vacuole 
Spheroid cavity in which food particles from the cytopharynx are digested.