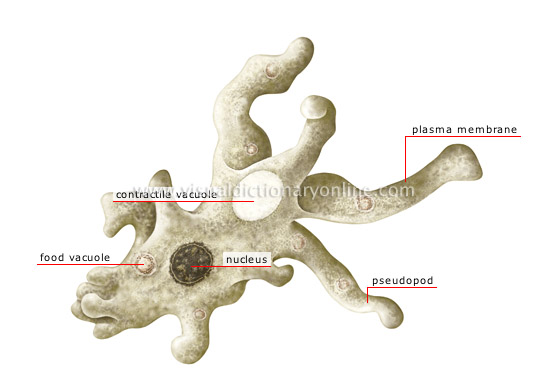
amoeba
Variably shaped one-cell organism, found in freshwater or salt water, in humid soil or, sometimes, as a parasite of animals. It moves about and feeds with the help of pseudopodia.
plasma membrane 
The cell’s flexible outer casing; it separates the cell from the surrounding environment and works as a filter to control the entry and exit of certain substances.
pseudopod 
Extension of the cytoplasmic membrane and cytoplasm allowing the amoeba to move about and to trap its prey.
contractile vacuole 
Spheroid cavity acting as a pump to evacuate excess water and waste from the cell.
nucleus 
Organelle containing a cell’s genes and controlling its activities.
food vacuole 
Spheroid cavity in which the amoeba traps its prey to digest it.