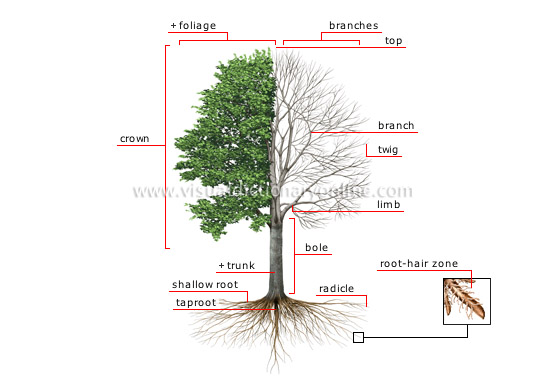
structure of a tree
The tree is composed of an underground part, the roots, and two aboveground parts, the trunk and the crown.
trunk 
Main part of the tree extending between the soil and the lower branches.
bole 
Part of the tree trunk extending between the stump and the first lower limbs; it has no offshoots.
limb 
Offshoot growing directly out of a tree trunk, subsequently dividing into branches and twigs.
twig 
The most slender offshoot of a tree branch.
crown 
Part of the tree above the trunk, including the branches and the foliage.
radicle 
The most slender offshoot of a tree root.
shallow root 
Root, often having many offshoots, growing somewhat horizontally into the rich moist topsoil.
taproot 
First root growing out of the seed that grows vertically into the soil; it usually has few offshoots, its main function being to anchor the tree in the ground.
branch 
Offshoot of one of the tree’s limbs.
top 
Apex of the tree’s crown.
branches 
The aggregate of larger and smaller branches that provide support for the tree’s leaves, flowers and fruit.
foliage 
The aggregate of the leaves on a tree; it is especially adapted to capture light and perform photosynthesis.
root-hair zone 
Part of the radicle covered in small absorbent hairs that ensure the tree is supplied with mineral salts and water.